
中學生也能科研:湖南師大附中6名學子科研成果在第十屆國際宇宙日活動中做分享
中學生也能科研
湖南師大附中6名學子科研成果在第十屆國際宇宙日活動中做分享
華聲在線11月20日訊(通訊員 李湘黔)11月10日,在國際宇宙日ICD上,年輕人成為天體粒子物理學的研究人員。來自世界各地的超過13個國家的中學、大學和研究機構等60多個研究小組參加了這個活動,世界各地的年輕人通過實驗,對不被我們注意到的宇宙粒子進行研究。參與者親身體驗如何探索宇宙射線的過程,了解天體粒子物理學的前沿科學。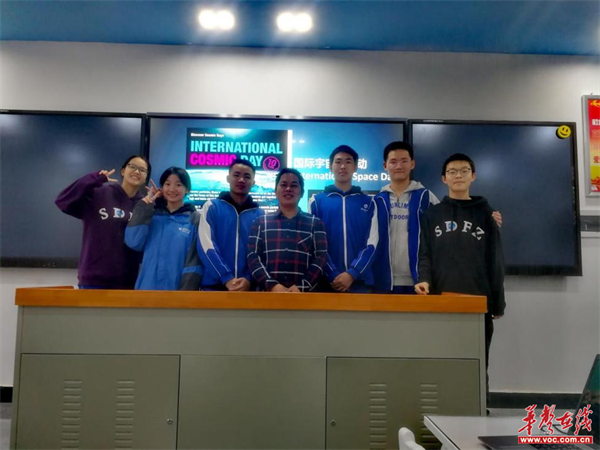
湖南師大附中師生積極參與國際科研交流活動。11月初,該校劉一帆、陳輝飏、袁嘉琪、張懷仁、左宏康、馬海鵬等同學在馬順存、楊一鳴、沈長銓、趙洪明老師的指導下參加了第十屆國際宇宙日活動,經過近10天的學習,初步了解了宇宙射線的基本知識,掌握了科學的研究方法,觀察分析數據并確定研究方向。同學們做出了可能的猜想,并通過分工合作討論、查找資料證明猜想的科學性。最終將研究成果轉化為論文,并于11月10日晚與國際友人展開視頻交流,分享研究成果、交換各自想法、互相解答疑惑。湖南師大附中6名學子科研成果受到充分肯定。

目前,中國已有“中國科學院高能物理研究所”“中國人民大學附屬中學”“北京市東直門中學”“湖南師范大學附屬中學”“江蘇省姜堰中學”和“江蘇省興化中學”等學校和研究所的相關課題組報名參加了ICD的視頻活動,并且在會上作了相關報告。通過本次活動,同學們收獲了友誼,增強了團隊合作意識,了解了現代科學前沿知識,也學會了科學研究的方法。

近年來,湖南師大附中積極開展科技創新教育,把科創課程作為學校卓越校本化課程精心打造,科技創新成果顯著,學校正朝著研究型卓越學校的奮斗目標邁進。
附1:研究論文
EAS Changed With Zenith Angle
Researchers: Liu Yifan, Yuan Jiaqi, Chen Huiyang, Ma Haipeng,Zhang Huairen, Zuo Hongkang.
Instructor: Ma Shuncun.
The High School Attached To Hunan Normal University
Ⅰ.Background
Cosmic rays usually consist of high-energy particles from space. On the way high-energy cosmic rays shoot from space to earth, they need to pass through the atmosphere and it is the time that they interact with atomic nuclei in the atmosphere, knocking out various secondary particles. These secondary particles will interact with atomic nuclei in the atmosphere again during the flight, producing more secondary particles, which are sprinkled from the air to the earth like a rainstorm, and conducting cascade reactions continue to occur in this way. This process is also known as "air shower". More specific, these secondary particles produced by cosmic rays repeatedly act to produce more secondary particles until the average energy is equal to a certain critical value, and the number of secondary particles reaches the maximum value, which is called shower maximum. After that, the particles gradually decay or are affected by the atmosphere. Absorption, so that the number of secondary particles gradually decreases.
High-energy cosmic rays can form "showers" with large area, which produce a large number of secondary charged particles reaching the ground almost simultaneously. By measuring these charged particles arriving at the same time, the "shower" cases can be obtained. Scientists usually study on cosmic rays by indirectly detecting these "showers" reaching the surface of the earth. In general, the higher the energy of cosmic rays, the larger the shower area that reaches the surface. In practical experimental setup, detector array are often used for detection.
In this article, we analyzed the data detected by the detector array of Dongzhimen Middle School in Beijing, China(39.933°N latitude, 116.417°E longitude, 46.4 meters above sea level). The detector array is composed of 9 scintillation detectors, separated by 10 meters, set in a 3×3 matrix pattern, and the sensitive area of each detector is 0.5 square meters.
Ⅱ.Data processing and analysis
We analyzed the direction of each EAS event within 5 days since 0:00 Beijing time on October 4, 2021, and obtained the number of events Ni with the uniform range of the zenith angle from 0 to 90° when i=9. Its standard error σi=Ni0.5. For the zenith angle range A to B, it covers a solid angle Ω=2π(cosA-cosB), and the effective area of the array is 400m2×COSθi (θi is the median of the zenith angle range i). In this way, we get the average EAS intensity Ii=Ni÷(3×Ωi×COSθi) within the unit solid angle range of each zenith angle within a day. The standard error is σli=σi÷(3×Ωi×COSθi). The following is the table after measurement and data processing (Table 1):
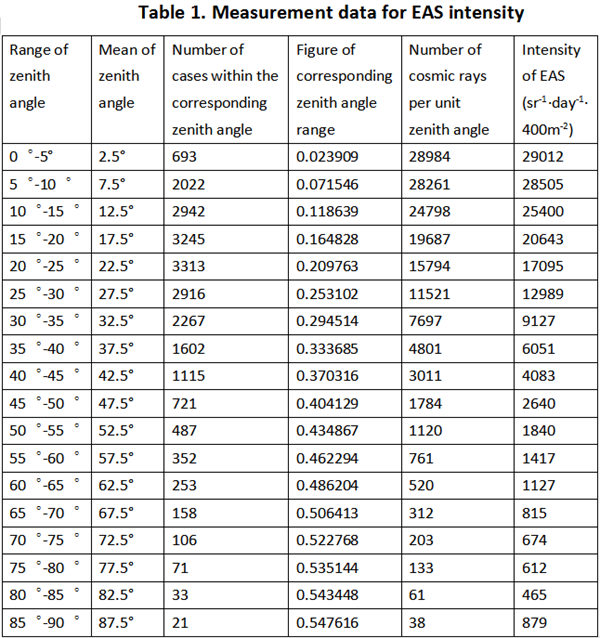
We expect the curve decrease monotonically at in the region (0°, 90°), however from data analysis the intensity of EAS takes the minimum value around (75°, 85°) and get slightly increase in the region (85°, 90°). The reason may relate to accidental coincidence fake events taken account into detection due to relatively large coincident time window.
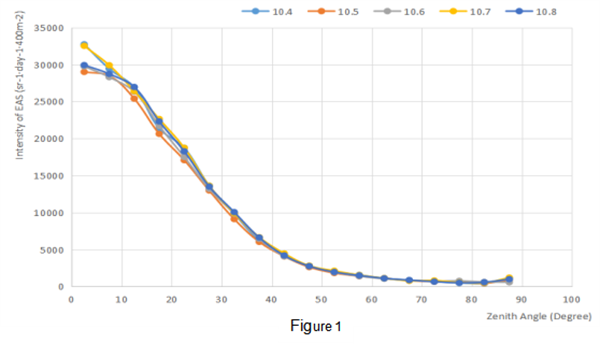
Ⅲ.Research discussion and result
From the data analysis, we can easily tell that the number of events within the corresponding zenith angle range always reaching the maximum value around X ∈ (20°, 25°) as shown in Figure 1. We believe that: on the one hand, as the zenith angle increases, the solid angle Ω, equals to 2π(cosA-cosB), is increasing, resulting in an increase in the number of events within the corresponding zenith angle; on the other hand, as the zenith angle increases, the effective detection area (0.5m2*cosX) of the detector decreases. Under the combined influence of these two factors, number of events within the corresponding zenith angle will achieve the maximum value at a certain angle position.
In the analysis of the curve of Intensity of EAS, we found that the curve varies steeply with the zenith angle at the beginning and the latter part is relatively flat as shown in Figure 2. From this result, we believe that: according to the principle of extended atmospheric shower, as the zenith angle increases , the particles need to pass through a thicker atmosphere and the primary particles need more energy to reach our detection threshold after being dispersed. Besides, the intensity of the isotropic primary cosmic ray is approximately proportional to E-2, so the EAS intensity is a descending function of the zenith angle.
Second to that, we found that the curve of Intensity of EAS changing with the zenith angle tends to take the minimum value around (75°, 85°) as shown in Figure 2. We believe that the slightly increase of intensity in the region (85°, 90°) may relate to accidental coincidence fake events taken account into detection due to relatively large coincident time window.
Last but not the least, in general, within EAS (Extensive Atmospheric Shower), the number of cosmic rays after area correction decreases as the zenith angle increases (ignoring accidental coincidence fake events)
附2:活動證書:






 |
華生在線新聞鏈接 |
湘ICP電子備案05014582號
